Firefighting is an essential public service that quite literally saves lives. The demand for firefighters in both the public and the private sector has increased in recent years, and this has called for more people to seek out trained professionals who can respond to emergency situations and fire outbreaks. If you’re interested in becoming a reservist volunteer firefighter, or even a full-time professional firefighter, then read this article to understand what kind of information you’ll be engaging with throughout your firefighting course, and how it’s relevant in South Africa.
Firefighting Principles
EMCARE’s firefighting courses teach students how to uphold 3 basic principles of firefighting. Firstly, students will learn how to participate in fire prevention procedures and training operations. Secondly, they will learn how to conduct regular maintenance and the upkeep of the fire station, as well as its equipment and instruments. Thirdly, they will learn how to respond effectively and timeously to medical emergencies, fire alarms, urban rescues and any other calls to protect people and infrastructure, including scenarios involving hazardous materials.
Fire Causes
During your participation in EMCARE’s firefighting courses, you’ll be introduced to important theories regarding common causes of fire and the different types of injuries and trauma related to fire outbreaks. You will learn how to academically identify these issues, as well as how to practically resolve them. Below are two lists that outline some of the theories in EMCARE’s course.
Common causes of fire
- Children playing with matches
- Burning oil on stovetops
- Gas leaks
- Faulty electrical blankets
- Unsafe or unattended fireplaces
- Embers from discarded cigarettes or tobacco products
- Unattended burning candles
- Open flames in dry areas
- Frayed electrical wires
- Faulty heaters
- Parrafin explosions
- Faulty appliances
Types of Burns
- Fire
- Thermal and scalding
- Chemical
- Radiation
- Electrical
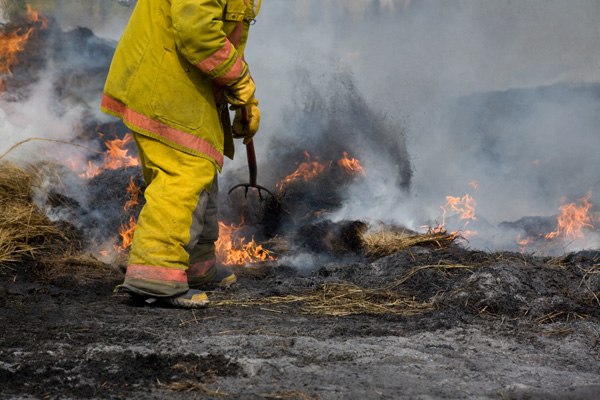

Key Duties
Students of EMCARE’s firefighting course will quickly learn that firefighters are expected to handle a range of tasks every day. These duties are expected to be conducted rigorously even under stressful environments. Firefighters should be good problem-solvers, quick thinkers and courageously proactive people with good initiative. Below is a list of some of the duties that students of the course can expect to learn about and practice.
- Identifying fire hazards
- Risk assessments
- Emergency planning
- Firefighting training
- Rescue and safety training
- Firewatcher training
- Safety inspections
- Fire prevention
- Fire suppression
- Fire engineering
- Emergency responses
- Medical and rescue response
- Medical aid assistance
- Call receipt and processing
- Vehicle and equipment maintenance
- Incident management
- Pre-fire planning
- Fire safety functions
Equipment
Throughout your firefighting course, you’ll come into contact with a range of new equipment and technology that is used in rescue operations and drills. EMCARE’s firefighting course convenors will be able to help you familiarise yourself with some of the many instruments that firefighters utilise on a daily basis. Below is a list of some of the pieces of equipment and other resources that you might come into contact with throughout your firefighting course.
- Power generators
- LED lighting systems
- HAZMAT equipment
- Thermal imaging cameras
- Hoses
- Nozzles
- Protective boots
- Protective clothing
- Firefighting gloves
- Warning alarms
- Proportioners, fittings and couplings
- Firefighting helmets
- Fire blankets
- Fire hydrants
- Fire extinguishers
- Respiratory and chemical protection equipment
- Proportioners, adapters and distributors
- Extinguishing agents
- Rescue equipment
- High-performance fans
- Fire trucks
- Submersible pumps
Relevant Legislation

The Fire Brigade Services Act is the main piece of legislation that determines fire standards and codes of practice in South Africa. During the theoretical phases of your firefighting course, you will learn about the FBSA as well as a whole other variety of legal implications that stem from the following pieces of legislation. While this list is not exhaustive, it does provide a sound example of the legal context in which firefighters must function. These acts are aligned with the Constitution, and they work in collaboration with the Fire Brigade Services Act.
- Fire Brigade Services Act, 1987 (Act No. 99 of 1987) (FBSA)
- National Veld and Forest Fire Act, 1998 (Act No. 101 of 1998)
- National Water Act, 1998 (Act No. 36 of 1998)
- Occupational Health and Safety Act, 1993 (Act No. 181 of 1993)
- Disaster Management Act, 2002 (Act No. 57 of 2002)
- Safety at Sports and Recreation Act, 2010 (Act No. 2 of 2010)
- National Environmental Management Act, 1998 (Act No. 107 of 1998)
- Major Hazardous Installation (MHI) Regulations;
- Criminal Procedure Act, 1977 (Act No. 51 of 1977)
- National Building Regulations and Building Standards Act, 1977 (Act No 103 of 1977)
- National Environmental Management Act, 1998 (Act No. 107 of 1998)
- Public Finance Management Act, 1999 (Act No. 1 of 1999)
- Municipal Finance Management Act, 2003 (Act No. 56 of 2003)
- Municipal Systems Act, 2000 (Act No. 32 of 2000)
- Municipal Structures Act, 1998 (Act No. 117 of 1998)
Employment

Participating in a firefighting course presents a good opportunity for upskilling and eventual employment. During your firefighting course, you will learn to master your physical skill, foundational and theoretical knowledge, as well as your practical work experience. EMCARE’s firefighting course educates students thoroughly so that they can be prepared for all of the occupational hazards and dangers involved in the field.
Throughout the firefighting course, students will learn about technological equipment, operational procedures and drills, staff hierarchies and the general working environment. After completing the course, students will be well-prepared to enter the profession with confidence and practical abilities. Firefighters have the option of working as reservists on a volunteer basis or as advanced professionals on a permanent basis.
Every fire department and institution has its own requirements when it comes to employing new staff. However, the general expectations for firefighters in South Africa are a matric certificate, a driving license, and a certificate of qualification from a firefighting course provided by an accredited institution like EMCARE. In a firefighting course, participants are also generally required to be unafraid of small enclosed spaces and heights, as these are common conditions in which firefighters must function.
Professionals who have graduated from firefighting courses such as EMCARE’s Advanced Fire Fighting Course (AFF) can expect to achieve career growth as they graduate from one position to the next. Fire departments have hierarchical staff structures, with the first position after examinations being that of a Platoon Commander. Thereafter, firefighters can look forward to being promoted to Station Commander, Divisional Chief, Deputy Chief and finally Chief.
Being a firefighter is a difficult job, as it requires you to work under stressful and often traumatic conditions. However, the work can be highly rewarding once you see how your personal sacrifices can contribute to the survival of innocent people. Participating in a firefighting course means that you will be able to serve your community.
Students who graduate from EMCARE’s firefighting course have the opportunity to either volunteer or work permanently, so if you choose to work as a professional firefighter then you can seek employment either from municipal fire departments or private firms. As a result of increasing fires around South Africa (such as the fire outbreak at the Bank of Lisbon in Johannesburg, the fire on the City of Cape Town’s mountain, and the fire at the National Assembly building in Parliament), the demand for trained professionals and firefighting course graduates has increased. So, new faces to the profession can expect to find a plethora of employment opportunities.
Section 5.2 of the Health and Environmental Regulations Act stipulates that employers must provide firefighting facilities in all vulnerable areas and as instructed by engineers, mark escape routes, and instruct workmen in fire precautions and the use of firefighting equipment amongst other legal requirements. Furthermore, all employers are required to ensure that at least 1 out of 50 employees in an organisation understands basic firefighting. This means that even if you choose not to pursue full-time professional firefighting, you will still have an increased chance of employment since you are well-trained for emergency scenarios.
Employers will be impressed with your ability to manage emergency situations and act calmly when affronted by danger. You can assure potential employers that your skills and professional firefighting course qualifications are a valuable asset in their company. For example, you can offer to use your firefighting course knowledge to assist them with conducting regular fire drills, informing staff of basic fire fighting skills, drafting evacuation procedures and assessing safety or fire risks.

The Importance of Fire Safety:
Fire-related deaths and injuries are pervasive in South Africa. Deaths caused by fires and fire-related burns make up 300 000 deaths annually. Despite the invention of fire-prevention tactics such as smoke detectors and flame retardants, mortalities and severe burns are still very apparent in low and middle-income areas such as South Africa. This is because the availability of safety measures is low, and because public services such as municipal fire departments are generally ill-equipped to manage high rates of fire.
In South Africa, fires are particularly pervasive due to high temperatures. In KwaZulu-Natal during the Winter seasons, citizens can expect to see large increases in the number of fire emergencies. Including bush fires and wildfires that lead to traumatic injuries and incidents such as third-degree burns, accidental fuel ingestion smoke inhalation. Fires also tend to break out in poorer communities as a result of haphazard urban development. Rapid urbanisation is often coupled with inadequate electricity supply, and as a result, you see residents using highly-flammable paraffin and bio-mass fuels as their main sources of energy.
The Fire Protection Association of South Arica’s 2015 report on deaths by fire demonstrated that 436 people died and that more than half of those deaths happened in informal dwellings. According to the Department of Health, South Africa has one of the highest levels of death and disability from injury in the world, and the fire-related burn death rate is greater than the world average. These fires also have extreme financial consequences, causing massive losses in a variety of industries. These fires are a threat to livelihoods, infrastructure and gross-domestic-product growth.
Similarly, education levels are also reduced in lower-income communities and thus many citizens are not informed about fire safety. This makes prevention more difficult, and so it is vital that there are firefighters who are well-trained and adequately prepared to respond to emergency situations effectively. The provision of EMCARE’s course is a step towards improving public fire safety and minimising the loss of life.
While it is of the utmost importance to avoid mortalities, it is also important to consider how fire-related injuries and burns can leave traumatic scars on people both physically and mentally. Those who have encountered fire outbreaks and burns will be forced to live with disabilities and disfigurements that could cost them their mental health and even their physical ability to work and participate in the economy. What’s more, prolonged periods of hospitalisation, trauma counselling, medical treatment, skin grafts and physiotherapy are costly procedures that many people in South Africa simply cannot afford.
Without sufficient social services or public facilities to care for these victims, survivors may find themselves as victims of debt, unemployment, social stigma, anxiety, post-traumatic stress, and depression. These kinds of social ills can be avoided when trained professionals and expeditious firefighters respond timeously to prevent fires from escalating and harming bystanders. By taking EMCARE’s firefighting course, you can be a part of the brave team of people who serve South Africans in the face of danger.















